Transmission: AT, DCT, or CVT – Which One Fits You Best?
When it comes to driving, the transmission might not get much attention, but it plays a vital role in your vehicle’s performance and driving experience. So, how many types of transmissions are there? What are the pros and cons of each?
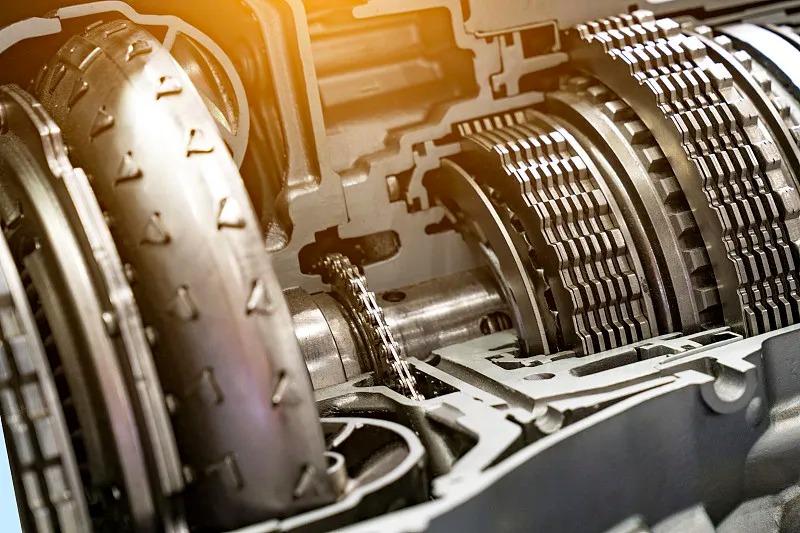
Today, let’s dive into the three most common transmission types: AT (Automatic Transmission), DCT (Dual-Clutch Transmission), and CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission).
Automatic Transmission (AT)
The AT, is one of the most traditional and widely used types. It uses a torque converter to shift gears automatically based on speed and engine load.
Advantages:
- Easy to drive: No need for manual gear shifts, perfect for city traffic.
- Smooth shifting: Offers a seamless ride with minimal gear change shock.
- Highly adaptive: Adjusts to road conditions and driving habits intelligently.
- Reliable: Durable structure with lower failure rates due to torque converter design.
Disadvantages:
- Power loss: The torque converter can cause some energy loss, especially during high-load driving.
- Complex structure: More components mean higher maintenance costs.
- Higher cost: Generally more expensive due to technology and licensing.
Best for: Drivers with a larger budget who prioritize comfort and reliability.
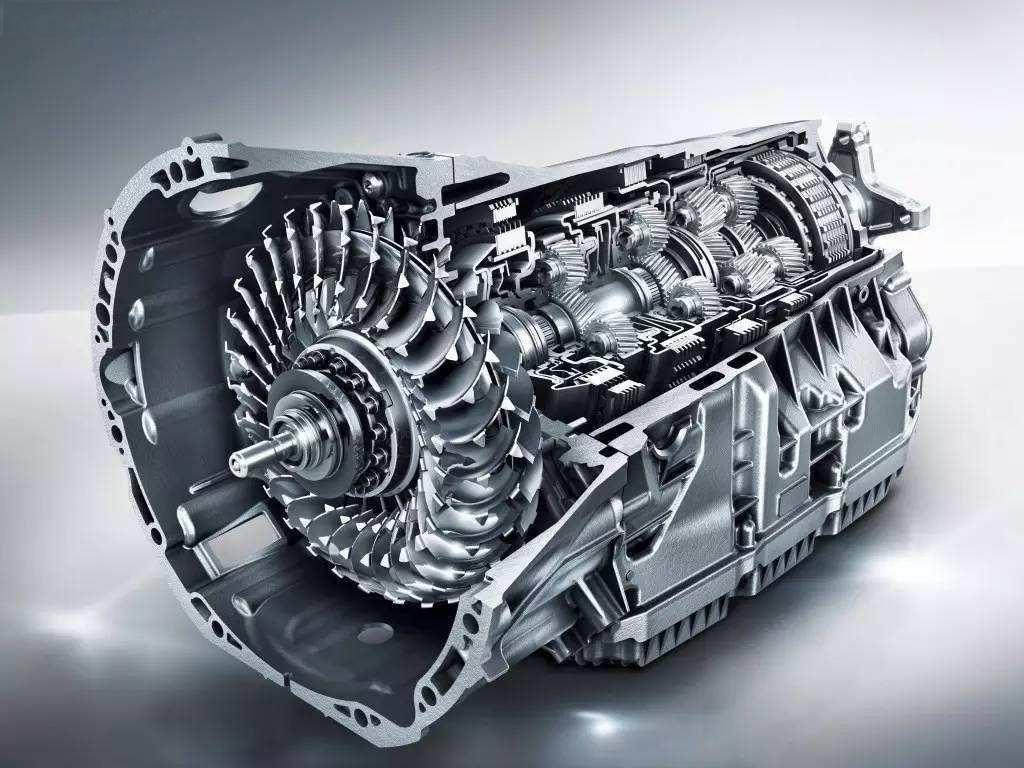
Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT)
The DCT, works like an advanced manual gearbox. It uses two separate clutches to control odd and even gears for lightning-fast gear shifts.
Advantages:
- Ultra-fast shifting: Changes gears in milliseconds, enhancing performance.
- Efficient: Delivers better fuel economy thanks to direct power transfer.
- Sporty feel: Ideal for driving enthusiasts who enjoy precision and speed.
Disadvantages:
- Jerky at low speeds: Can feel rough in stop-and-go traffic.
- Maintenance concerns: More delicate and costly to repair or service.
Best for: Those who frequently drive on highways or prefer spirited driving on smooth roads.
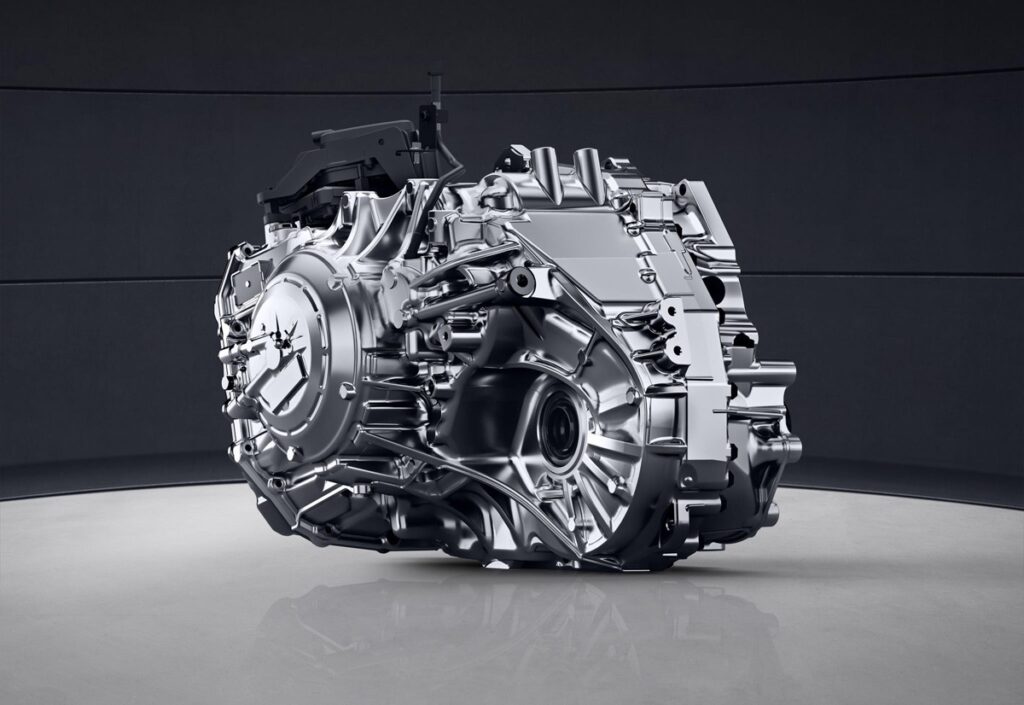
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
The CVT, uses belts and pulleys instead of fixed gears. This allows it to seamlessly adjust engine speed without traditional gear shifts.
Advantages:
- Exceptional smoothness: No shift shock—perfect for daily city driving.
- Fuel-efficient: Keeps the engine at optimal RPM for lower fuel consumption.
- Low maintenance: Simple design means fewer mechanical issues.
Disadvantages:
- Sluggish response: May feel underpowered during rapid acceleration.
- Durability issues: Prolonged high-load usage can impact its lifespan.
Best for: City commuters who value fuel savings and comfort, especially with small-engine vehicles.

Which Gearbox Is Better?
That depends on your driving style and needs.
- Prefer convenience and comfort? AT is a solid choice.
- Love performance and control? DCT brings excitement to the road.
- Focused on fuel economy and everyday ease? CVT could be your best match.
In conclusion, there’s no “best” transmission—only the best for you. Try test-driving different models and experience how each transmission performs in real scenarios. We hope this guide helps you make an informed decision and enjoy every journey behind the wheel.
If you have a need to buy a used car, or if you run a used car business, we’re here to help. As a leading exporter with over 20 years of experience, DDong Used Cars offers a wide range of vehicle brands (100+), efficient logistics, and after-sales support.
Contact us today to learn more. Simply let us know what you’re looking for, and we’ll provide you with an unmatched sourcing experience. Explore our news section for more automotive insights and tips for running a successful dealership.







