Drivetrain Types Explained: FWD, RWD, and AWD Differences
Introduction: Understanding Drivetrain Types
Drivetrain Types play a major role in how a car drives, accelerates, turns, and handles different road conditions. Many drivers only see the wheels, yet the real difference lies in how the engine and transmission deliver power.
This guide explains front-wheel drive (FWD), rear-wheel drive (RWD), and all-wheel drive (AWD) in simple terms. Moreover, you will learn their advantages, disadvantages, and which one fits your daily driving style. After reading, you will know exactly how different Drivetrain Types affect comfort, safety, and performance.
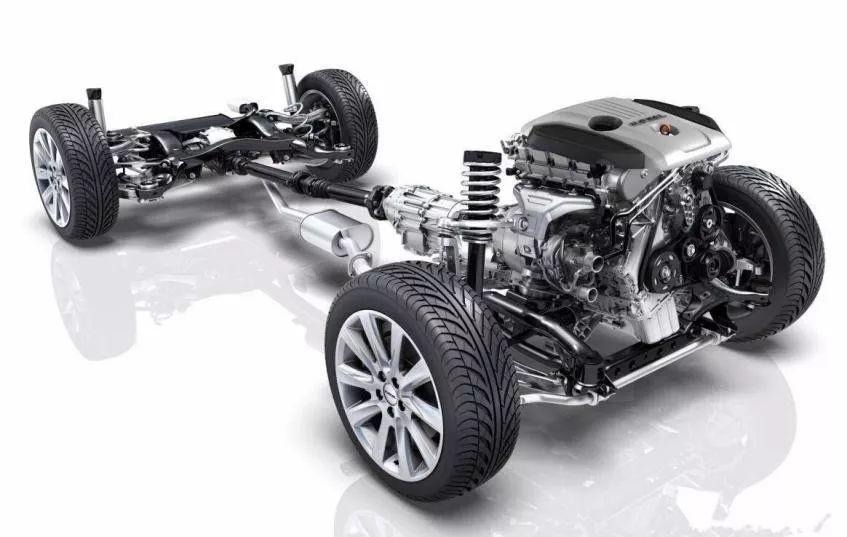

1. What Is Front-Wheel Drive (FWD)?
In front-wheel drive, the engine is usually installed sideways. It sends power directly to the front wheels, and these wheels pull the car forward. This setup also places the engine and gearbox together at the front.
Advantages of FWD
- Better fuel economy:
Power goes straight to the front wheels. Therefore, fewer parts are needed, and energy loss stays low. - More space inside the cabin:
Since the transmission and differential share one housing, the layout uses less room. This gives passengers more space. - Lower cost and weight:
Fewer components make the car cheaper and lighter. - Good traction in rain:
The weight of the engine sits over the driven wheels, improving grip on wet roads.
Disadvantages of FWD
- Understeer in sharp turns:
The front becomes heavy, which may cause the car to slide forward in tight corners. - Front tires wear faster:
They handle both steering and acceleration. - Less balanced handling:
The uneven axle length and front-heavy layout reduce sporty performance.
Who Should Choose FWD
FWD is ideal for daily commuting, family use, and urban driving. It offers good efficiency and comfort.
Examples: Toyota Corolla, Honda Civic, VW Lavida, Honda CR-V, BYD Song Pro.

2. What Is Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD)?
In rear-wheel drive, the engine is mounted lengthwise. Power travels through a driveshaft to the rear wheels. These wheels push the car forward, while the front wheels are responsible only for steering.
This is the classic layout used in many performance and luxury vehicles.
Advantages of RWD
- Better handling balance:
Steering and power delivery are separated, giving smoother control. - Improved acceleration:
When a car accelerates, weight shifts to the rear, increasing traction. - Less tire wear in front:
Front wheels steer but do not deliver power. - More engaging driving experience:
RWD cars corner well and feel more stable at higher speeds.
Disadvantages of RWD
- Heavier and more complex:
The driveshaft and rear differential add weight and cost. - Less space inside:
The longitudinal setup takes up room. - Reduced traction in snow:
Without engine weight on the driven wheels, grip decreases on slippery surfaces.
Who Should Choose RWD
RWD suits drivers who want sporty handling, strong acceleration, and a more balanced driving feel.
Examples: BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Cadillac, Li Auto.
Note: RWD comes in variants such as front-engine RWD (FR), mid-engine RWD (MR), and rear-engine RWD (RR).

3. What Is All-Wheel Drive (AWD or 4WD)?
All-wheel drive sends power to all four wheels. As a result, the car gains strong traction, stability, and control on rough or slippery surfaces.
Advantages of AWD
- Maximum grip:
Power shared among all wheels improves performance on wet, snowy, or uneven roads. - Greater stability:
The system enhances cornering and acceleration. - Ideal for off-road or performance vehicles:
It supports strong power output and safe driving in challenging conditions.
Disadvantages of AWD
- Higher fuel use:
More parts create extra weight and friction. - Higher cost and complexity:
Repairs and maintenance can be more expensive.
Who Should Choose AWD
AWD is ideal if you want stability, safety, and all-weather reliability. It suits mountain roads, winter climates, and light off-roading.
Examples: Audi Quattro models, Subaru, Toyota RAV4 AWD, BMW xDrive, Tesla Dual Motor.

4. How to Choose the Right Drivetrain Type
Choosing the best option depends on your driving habits, climate, and priorities.
| Driving Need | Best Drivetrain Type | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Daily city driving | FWD | Efficient and spacious |
| Performance driving | RWD | Balanced and responsive |
| All-weather safety | AWD | Best traction and control |
Moreover, no drivetrain is perfect for everyone. Each has its own strengths, and the right choice depends on your lifestyle.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Drivetrain Types for You
Now you understand how the main Drivetrain Types — FWD, RWD, and AWD — differ in structure and behavior.
Front-wheel drive offers space and efficiency. Rear-wheel drive provides dynamic handling. All-wheel drive delivers safety and grip.
In the end, the best choice is the one that matches your driving style and daily needs.
With this knowledge, you can confidently choose the drivetrain type that suits you best.
If you have a need to buy a car, or if you run a car business, we’re here to help. As a leading exporter with over 20 years of experience, DDong Used Cars offers a wide range of vehicle brands (100+), efficient logistics, and after-sales support.
Contact us today to learn more. Simply let us know what you’re looking for, and we’ll provide you with an unmatched sourcing experience. Explore our news section for more automotive insights and tips for running a successful dealership.