Brake Disc: Types, Principles, and Materials Explained
The brake disc, also known as a rotor, is a critical part of a vehicle’s braking system. It works hand in hand with brake pads to slow down or completely stop the car. By converting kinetic energy into heat, brake discs make driving safer and more reliable.
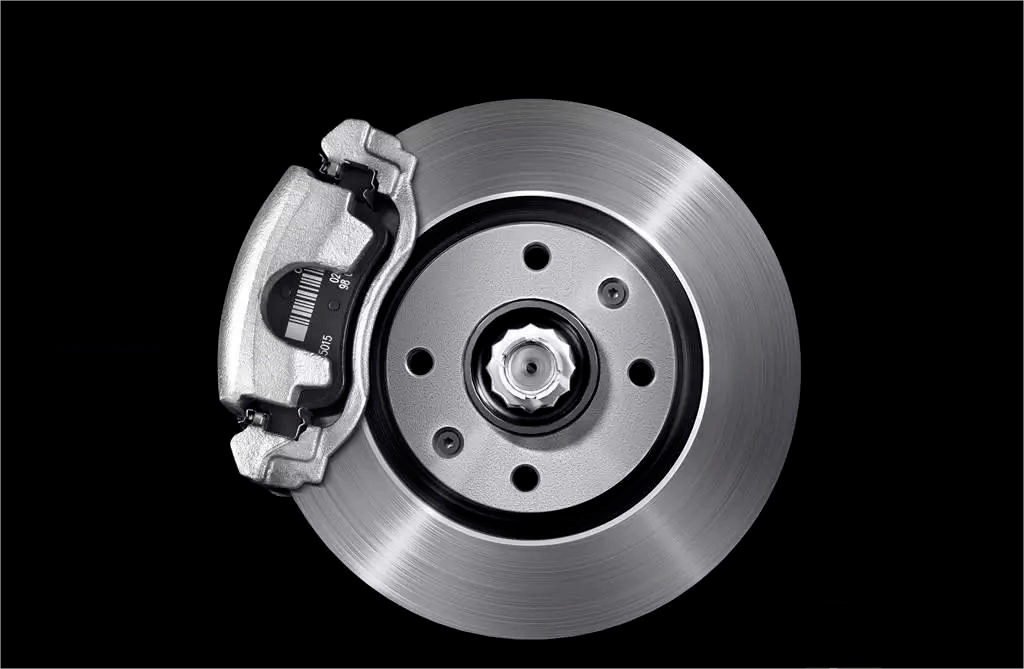

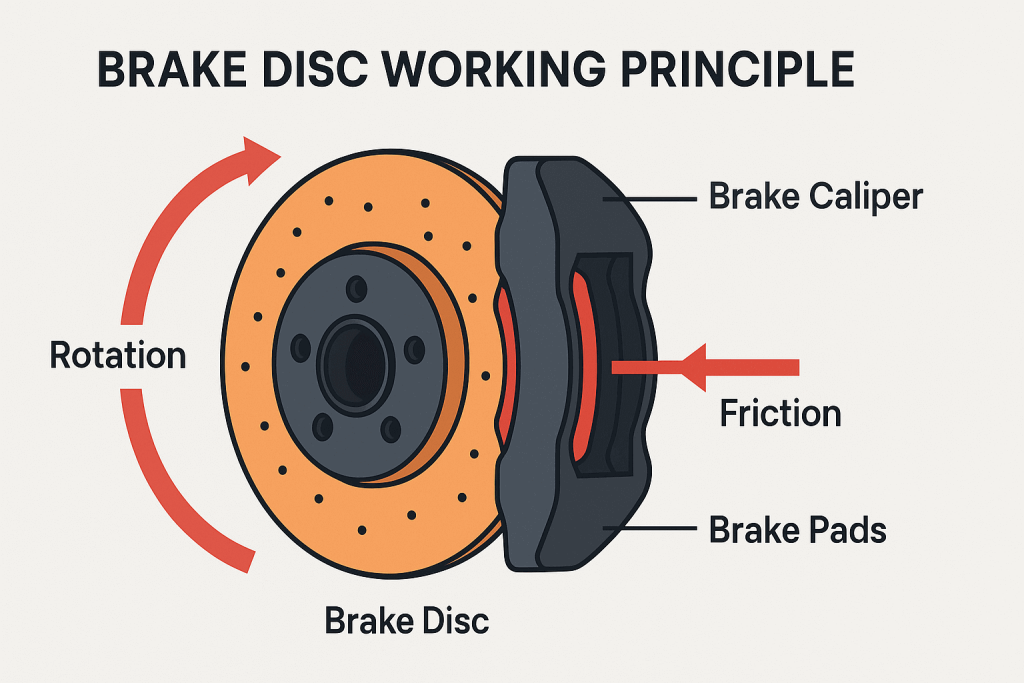
How Brake Discs Work: The Basic Principle
Friction and Heat Dissipation
When you press the brake pedal, hydraulic pressure pushes the brake pads against the spinning disc. The friction slows the car while heat is released.
Hydraulic Pressure and Caliper Action
The caliper acts like a clamp, squeezing brake pads onto the disc. The harder you press the pedal, the stronger the grip, and the quicker the stop.
Comparison with Drum Brakes
Unlike older drum brakes, discs offer:
- Faster cooling
- More consistent braking
- Less risk of brake fade
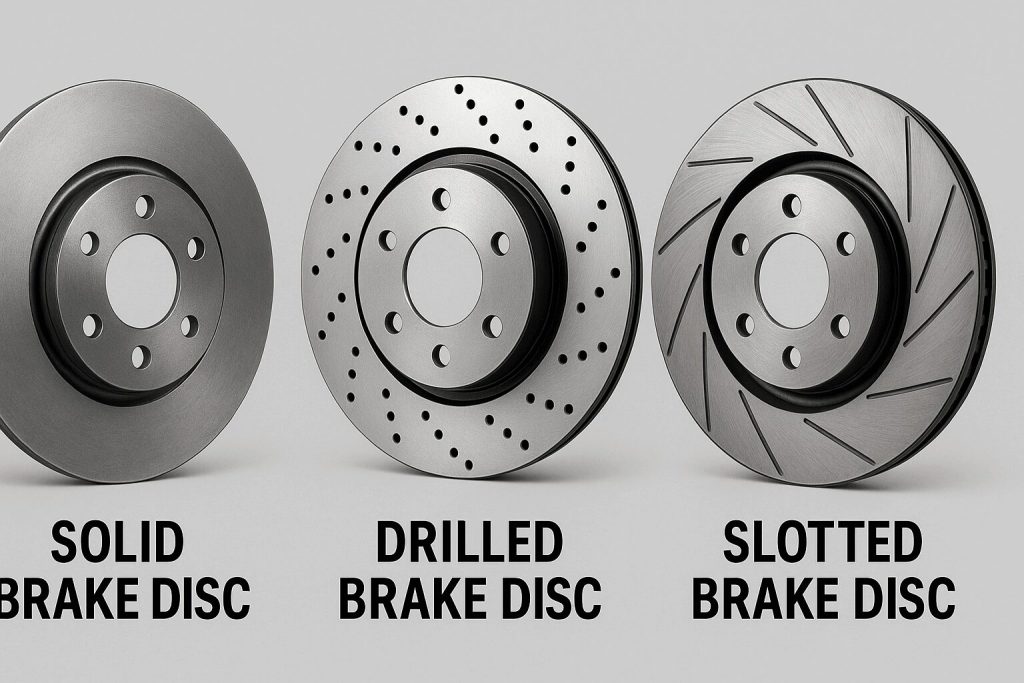
Types of Brake Discs
Solid Brake Discs
A simple design with a smooth surface. Affordable and durable, but less efficient at cooling.
Vented Brake Discs
Built with inner channels for airflow. These are common in sedans and SUVs due to better heat dissipation.
Drilled Brake Discs
Feature precision holes that help release heat and gases. Great for performance cars, but can crack under extreme stress.
Slotted Brake Discs
Grooved discs that sweep away dust, water, and debris. Perfect for wet or off-road driving.
Combination (Drilled & Slotted) Discs
Combine both benefits, widely used in racing and sports applications.

Materials Used in Brake Discs
Cast Iron Brake Discs
The most common type—affordable and reliable but heavy and prone to rust.
Carbon-Ceramic Brake Discs
Lightweight, extremely durable, and resistant to brake fade. Often used in supercars, but very expensive.
Steel & Composite Brake Discs
Offer a balance between performance and cost, commonly found in motorcycles and high-performance sedans.

Conclusion
Brake discs are vital for safety and performance. From solid cast iron to advanced carbon-ceramic, each type has its advantages depending on cost, driving conditions, and vehicle design. By understanding their working principle, types, and materials, drivers can choose the right brake system to ensure both safety and efficiency on the road.
If you have a need to buy a car, or if you run a car business, we’re here to help. As a leading exporter with over 20 years of experience, DDong Used Cars offers a wide range of vehicle brands (100+), efficient logistics, and after-sales support.
Contact us today to learn more. Simply let us know what you’re looking for, and we’ll provide you with an unmatched sourcing experience. Explore our news section for more automotive insights and tips for running a successful dealership.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What’s the difference between solid and vented brake discs?
Solid discs are cheaper and simpler, while vented discs cool faster and perform better under heavy braking.
2. Are drilled brake discs better for everyday driving?
Not necessarily. They look sporty and improve cooling, but they can wear faster and are more prone to cracks than solid or vented discs.
3. Why are carbon-ceramic brake discs so expensive?
They’re made from advanced materials that offer outstanding heat resistance and long lifespan—ideal for high-performance sports cars.
4. How long do brake discs last?
Typically between 30,000–70,000 km, depending on driving style and conditions.
5. Do electric cars use brake discs?
Yes, although EVs use regenerative braking, they still rely on discs for emergency stops and additional braking power.